Moulding of Bricks
Moulding of Bricks
Giving the required shape to the prepared brick earth is known as moulding of bricks. There are two different ways of moulding.
a) Hand moulding
b) Machine moulding.
a. Hand moulding:
Hand moulding of bricks is extensively used and could be done either on ground or on table.
b. Ground moulding:
This method is adopted when a large and level area of land is available for the purpose. The area of land on which moulding is to be done is levelled, plastered smooth and sprinkled over with sand.
- To prevent the moulded bricks from sticking to the moulds either sand is sprinkled on the inner sides of the mould or the mould is dipped in water each time before moulding is done. When sand is used to prevent the sticking of earth to moulds the moulded bricks are known as sand moulded and if the mould is dipped in water each time before moulding a brick then the bricks are known as slop moulded bricks. Sand moulded bricks have better finish and sharper edges.
- After either sprinkling sand on the inside of the mould or dipping the mould in water take a lump of well prepared earth, the volume of which is a little more than that of the brick. This lump is shaped in hands to the size and shape of the brick.
- Now it is rolled in sand and with a jerk the lump is dashed into the mould in such a manner that the mould is completely filled with earth. The moulder then gives blows with his fists and press in the corners and edges with the
thumbs. - The surplus soil is then scrapped off and the top surface is levelled. A metal plate with a sharp edge, known as strike is used for removing the surplus soil. Generally a thin wire stretched on a frame is used for this purpose.
- v. After the brick has been moulded the mould is given a gen stroke with something hard and then mould is lifted leaving the brick dry on the ground. The mould is placed nearby to mould another brick and the process is repeated.
Bricks moulded directly on the ground have their lower face rough and can have no frog. To avoid it bricks are moulded on a block of wood known as the moulding block, having a projection 0.5 cm thick. A moulder can mould between 500 to 1000 bricks per day.
c. Table Moulding:
In it the moulder carries out the moulding of brick on a table. He does so while standing by the side of the table. He moulds bricks on boards known as stock boards. Stock boards are of the same size as the moulds and have a projection for the frog. Sand is sprinkled inside the mould and on the stock board. The mould is placed to fit the stock board and then filled with earth. Sufficient quantity of earth is dashed into the mould pressed hard and the surplus earth is removed with a strike or a thin wire. A Pallet is then placed on the mould. The mould containing the brick is then smartly lifted off the stock board and inverted so that the whole rests on the pallet. The mould is then given a gentle blow and lifted leaving the brick on the pallet. One more pallet is placed on the brick and it is carried to drying site between the two pallets. It is allowed to dry on side.
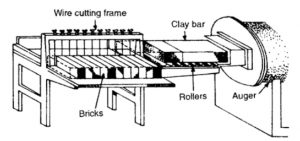
d. Machine moulding:
There are a variety of moulding machines and these machines are capable of manufacturing large number of bricks quickly. The bricks moulded in machine have better / sharp edges / smooth surface, stronger than hand moulded bricks etc.
1. Manufacturing of Bricks
2. Moulding of Bricks
3. Drying of Bricks
4. Burning of Bricks
5. Hoffmann’s kiln and Bull’s trench kiln
Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks, Moulding of Bricks

NICE TEACHING MESSAGE AND INTERESTING
Thanks