Cranes,Parts,Hazards
Cranes
Consists of a rotating structure for lifting and lowering on rubber tires or crawler treads.
Crane Parts
Hoist – Used to lift and lower load.
Boom – An inclined spar, strut, or other long member supporting the hoist
Jib – Extension attached to the boom point to provide added boom length for lifting specified loads.
Rigging Equipment Slings
Types of slings include alloy steel chain, wire rope, metal mesh, natural or synthetic fiber rope, and synthetic web.
How Do Accidents Occur?
- Instability – unsecured load, load capacity exceeded, or ground not level or too soft
- Lack of communication – the point of operation is a distance from the crane operator or not in full view of the operator
- Lack of training
- Inadequate maintenance or inspection
Major Causes of Crane Accidents
- Contact with power lines
- Overturns and Falls
- Mechanical failures
Who is at Risk ?
- Operators
- Persons at crane site
Load Limiting Factors for Cranes
- Not level
- Wind
- On its wheels
- Limits of wire rope, slings and lifting device
Competent Person
The competent person must inspect all machinery and equipment prior to each use, and during use, to make sure it is in safe operating condition. If it needs fixing, take it out of service and don’t use it until it is fixed.
Crane Hazards
- Improper loading
- Excessive speeds
- No hand signals
- Inadequate inspection and maintenance
- Unguarded swing radius
- Working too close to power lines
- Shattered windows
- No steps/guardrails walkways
- No boom angle indicator
1.Improper load
Improper loads or speeds can result in the tipping of the crane
2.Power Lines
Stay clear from power lines at least 10 feet
3.Hand Signals
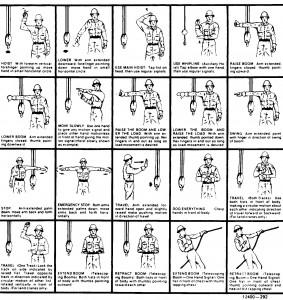
An illustration of the signals must be posted at the job site
4.Guard Moving Parts
Guard moving parts such as gears or belts
5.Swing Radius
Stay out of the swing radius of the crane – Make sure there are barrier guards showing swing radius
6.Operator Visibility
Make sure broken windows or other obstructions do not prevent the operator from seeing
7.Ladders
 Use ladders to get to the upper portion of the cab
Use ladders to get to the upper portion of the cab
8.Guardrails
Runways and steps need to have guardrails, handholds and slip resistant surfaces
9.Suspended Loads
10.Boom Angle Indicator
A boom angle indicator must be on the crane
11.Supporting Surface
Cranes must be on a firm supporting surface and level within 1 percent
12.Sheaves
13.Tire Inspections
Conduct regular inspections of tires for excessive wear or damage
SUMMARY
- An unstable load, lack of communication, lack of training, and inadequate maintenance or inspection are major contributors to crane accidents.
- Operators or others working in the area can be victims to “struck by” and “caught in” injuries.
- Contact with power lines causes many accidents.
- A competent person must inspect a crane regularly to insure it is in proper order.
- Planning and training reduces accidents.
Cranes,Parts,Hazards Cranes,Parts,Hazards Cranes,Parts,Hazards Cranes,Parts,Hazards Cranes,Parts,Hazards Cranes,Parts,Hazards